Smart home technology design for modern living
Introduction to Smart Home Technology Design
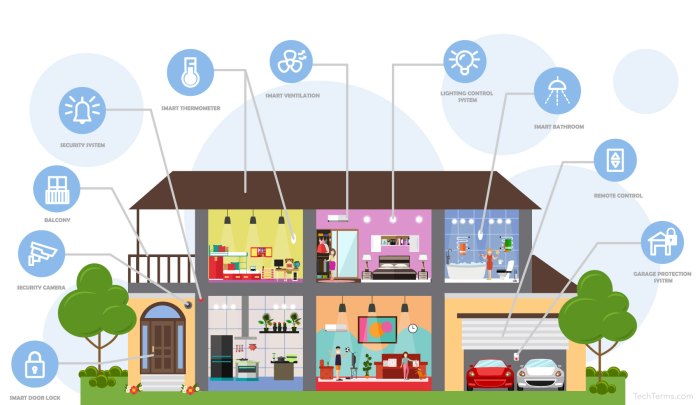
Smart home technology design – Smart home technology has progressed significantly over the past few decades, transforming the way we interact with our living spaces. Initially, automation was limited to basic tasks, but advancements in internet connectivity and artificial intelligence have made it possible to create highly interactive and responsive environments. This evolution underscores the importance of smart home technology in modern living, where convenience, security, and energy efficiency have become essential components of our daily routines.Key components that define smart home technology include devices such as smart speakers, thermostats, security cameras, and lighting systems.
These devices are interconnected through home networks, allowing users to manage them remotely via smartphones or voice commands. User experience plays a vital role in the design of these technologies, as it directly impacts how effectively users can interact with their smart homes. A well-designed user experience ensures that smart home systems are intuitive, accessible, and customizable, meeting the varied needs of diverse households.
Key Components of Smart Home Technology
Understanding the primary components of smart home technology is essential for appreciating its full potential. These components work together to create a cohesive smart home ecosystem. The main elements are:
- Smart Devices: These include appliances such as smart refrigerators, smart ovens, and smart locks that can be controlled remotely.
- Smart Hubs: Centralized systems that connect various smart devices, allowing them to communicate with one another and be controlled from a single interface.
- Wireless Technology: Protocols like Wi-Fi, Zigbee, and Z-Wave facilitate communication between devices and the hub, ensuring seamless operation.
- Mobile Applications: Apps that allow users to control smart home devices from their smartphones, providing convenience and remote accessibility.
- Voice Assistants: Technologies like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant enable voice control of smart devices, enhancing user interaction and accessibility.
The integration of these components creates an ecosystem where users can easily manage their home environment.
“A smart home is not just about technology; it’s about creating a seamless and enriching experience for the user.”
The Role of User Experience in Smart Home Design
User experience is critical in the design of smart home technology, as it determines how effectively users can engage with their devices. A positive user experience can lead to higher satisfaction and increased adoption of smart home technologies. Factors influencing user experience include:
- Intuitiveness: Users should be able to understand how to operate smart home devices without extensive training. Simple, straightforward interfaces are key.
- Customization: Users should have the ability to tailor their smart home systems to meet their specific needs and preferences, which enhances their connection to the technology.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Providing users with clear feedback on their actions, such as visual or auditory notifications, can improve their confidence in using smart devices.
- Integration: Seamless integration between different devices ensures a smooth user experience, allowing users to control multiple elements of their home environment effortlessly.
- Security: A strong emphasis on security measures within smart home systems fosters trust and encourages users to engage with the technology.
Incorporating these UX principles into the design of smart home technologies not only enhances functionality but also enriches the overall living experience, making smart homes more inviting and user-friendly.
Types of Smart Home Devices

Source: co.uk
Smart home devices have revolutionized the way we interact with our living spaces, offering enhanced convenience, security, and efficiency. These devices can be categorized into several key areas, each serving distinct functions that contribute to an integrated smart home experience. Understanding these categories helps homeowners make informed decisions about which devices best suit their needs.The various types of smart home devices include lighting systems, security products, heating and cooling solutions, and entertainment systems.
Each category has its unique functionality, allowing for seamless integration that enhances overall home automation. The following sections will Artikel these categories in detail, highlighting their purposes and the way they interact with one another.
Lighting Systems
Smart lighting systems allow users to control the brightness and color of their home lighting remotely or through automation. These systems can be programmed for various scenarios, such as dimming lights during movie nights or brightening them for morning routines. The key features include:
- Smart Bulbs: Energy-efficient LED bulbs that can be controlled via smartphone apps, voice commands, or integrated with other smart home systems.
- Smart Switches: Replace traditional light switches with smart ones that enable remote control and scheduling of lights.
- Motion Sensors: Automatically turn lights on or off when someone enters or leaves a room, enhancing energy efficiency.
Lighting systems are essential for creating ambiance and can be synchronized with other devices, such as security cameras, to enhance safety.
Security Devices
Security devices are critical for ensuring the safety of a home. They include various products that work together to provide comprehensive monitoring and protection. Key components are:
- Smart Cameras: Allow for real-time video surveillance accessible from smartphones, providing alerts and enabling monitoring from anywhere.
- Smart Doorbells: Feature built-in cameras and two-way audio that allow homeowners to see and communicate with visitors remotely.
- Smart Locks: Provide keyless entry through mobile apps, enabling better control over who enters the home and when.
The integration of these security devices allows for a cohesive system that sends alerts to users and even locks doors automatically when the homeowner is away.
Heating and Cooling Solutions
Smart heating and cooling systems significantly enhance energy efficiency and comfort levels in homes. These devices can learn user preferences and adjust settings accordingly. Important types include:
- Smart Thermostats: Learn the household’s temperature preferences and adjust heating or cooling schedules automatically to save energy.
- Smart Vents: Control airflow to different rooms, optimizing temperature based on occupancy and personal preferences.
- Smart Radiators: Provide individual control of heating in each room, allowing for tailored comfort and energy savings.
These systems work together to maintain optimal energy use while ensuring a comfortable living environment.
Entertainment Systems
Smart entertainment systems integrate various media devices to provide seamless user experiences. These systems allow for centralized control of audio and video components. Key elements are:
- Smart Speakers: Provide high-quality audio and can be connected to various services, allowing voice commands for music, news, and more.
- Smart TVs: Integrate streaming services and allow for voice control, offering a range of entertainment options at the user’s fingertips.
- Streaming Devices: Connect traditional TVs to the internet, enabling access to a wide variety of streaming platforms and applications.
The integration of these entertainment devices allows for easy control from a single app or voice command, enhancing the overall media experience in the home.
Design Principles for Smart Home Technology
The design of smart home technology is driven by several fundamental principles that ensure the systems are effective, user-friendly, and capable of meeting the diverse needs of their users. These principles focus on enhancing user experience, improving functionality, and creating seamless integration into daily life. As we delve into the core design principles, it becomes evident how important it is to prioritize user engagement and simplicity in the technology’s architecture and interface.The importance of user-centered design cannot be overstated in smart home technology.
This approach emphasizes understanding the user’s context and needs, ensuring that devices not only operate effectively but also enhance the user’s experience. On the other hand, technology-centered design focuses more on the capabilities and features of the technology itself, which can sometimes lead to complex user interactions. Below is a comparison of these two approaches to highlight their differences and implications in smart home technology design.
Comparison of User-Centered Design vs. Technology-Centered Design Approaches
A clear understanding of the contrasting perspectives of user-centered and technology-centered design can inform better development strategies for smart home technology. The table below Artikels key differences between these two approaches.
| Aspect | User-Centered Design | Technology-Centered Design |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | User needs and experiences | Technology capabilities and performance |
| Design Process | Iterative, based on user feedback | Linear, focused on specifications |
| Interface Complexity | Simple and intuitive | Can be complex with advanced features |
| Adaptability | Highly adaptable to user preferences | Less adaptable, often rigid in usage |
| Goal | Enhancing user satisfaction and engagement | Maximizing technological efficiency |
The best practices for creating intuitive interfaces and user interactions in smart home devices are crucial for ensuring that users can easily navigate and utilize their technology. An interface should be designed with clarity and minimalism in mind, avoiding clutter while presenting necessary information effectively. Here are key practices to consider when designing user interfaces:
Best Practices for Intuitive Interfaces and User Interactions, Smart home technology design
Creating an intuitive interface requires a deep understanding of how users interact with devices. The following points are essential for fostering positive user experiences:
- Simplicity in Design: Keeping the interface uncluttered allows users to focus on essential functions and reduces cognitive load.
- Consistency: Ensuring that navigation and controls are consistent across devices helps users apply their knowledge from one device to another effortlessly.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Providing instant feedback for user actions, such as visual or auditory cues, reinforces user confidence and enhances interaction.
- Customization Options: Allowing users to customize their interfaces or settings can lead to a more personalized and satisfactory experience.
- Accessibility: Designing with accessibility in mind ensures that all users, regardless of ability, can navigate and utilize their smart home technology effectively.
Integrating these best practices into the design of smart home technology not only enhances user satisfaction but also promotes wider adoption of these technologies across different demographics.
Integration and Interoperability Challenges: Smart Home Technology Design
Integrating various smart home devices from different manufacturers presents a unique set of challenges that can affect user experience and system functionality. As consumers increasingly adopt smart home technologies, understanding these challenges becomes essential for seamless operation and user satisfaction.The diversity in smart home devices often leads to compatibility issues, primarily due to the lack of standardized protocols. Different manufacturers may use proprietary technologies that do not communicate effectively with one another, resulting in fragmented ecosystems.
This issue can hinder the ability of users to control devices collectively, leading to frustration and limited functionality.
Challenges in Device Integration
Several common challenges arise when attempting to integrate smart home devices, including:
- Lack of Standardization: Many devices rely on proprietary communication protocols, which can make integration cumbersome and limit interoperability between devices from different manufacturers.
- Network Compatibility: Devices may operate on different frequency bands or wireless standards (such as Zigbee, Z-Wave, or Wi-Fi), complicating the integration process.
- Firmware Limitations: Regular firmware updates are necessary for optimal performance. However, manufacturers may not always provide timely updates, leading to potential security vulnerabilities or compatibility issues.
- User Experience Fragmentation: When devices from multiple brands are used, the user interface can become inconsistent, making it harder for users to manage their smart home effectively.
Importance of Standard Protocols
Standard protocols play a vital role in ensuring that devices from different manufacturers can communicate effectively. By adopting widely accepted communication standards, manufacturers can enhance interoperability and user experience.
“Standardized protocols enable seamless device interactions, providing a unified control system for users.”
Common protocols that promote interoperability include:
- Zigbee: A low-power wireless communication standard designed for smart home devices, enabling them to connect and communicate with ease.
- Z-Wave: Another wireless standard focused on home automation, allowing devices to work together regardless of the manufacturer.
- Wi-Fi: While primarily used for internet connectivity, many smart devices utilize Wi-Fi, making integration simpler for devices that support this standard.
- Thread: A relatively new protocol that enables secure and reliable communication between devices, enhancing the smart home ecosystem.
Solutions to Overcome Integration Challenges
To tackle the challenges of device integration and enhance interoperability, several solutions can be implemented:
- Adopting Universal Standards: Encouraging manufacturers to adopt universal protocols such as Matter can significantly improve compatibility across devices.
- Utilizing Hubs: Smart home hubs can act as intermediaries, allowing devices from different manufacturers to connect and communicate, simplifying user control.
- Regular Firmware Updates: Ensuring that manufacturers provide regular software updates can help to maintain security and compatibility with new devices.
- User Education: Providing resources and guides for users can empower them to understand their systems better, enhancing their ability to integrate and manage devices effectively.
Security and Privacy Considerations

Source: precondo.ca
In the rapidly advancing realm of smart home technology, security and privacy have emerged as significant concerns for users. As more devices connect to the internet and share personal data, safeguarding this information is crucial. This section delves into the various security risks associated with smart home technologies, methods for ensuring user privacy, and the implications of data collection within these environments.
Security Risks and Mitigation Strategies
The integration of smart devices into homes introduces potential vulnerabilities that can be exploited by cybercriminals. Common security risks include unauthorized access, malware infections, and data breaches. Here are essential strategies to mitigate these risks:
- Regular Software Updates: Keeping device firmware and applications updated is vital to protect against known vulnerabilities. Manufacturers often release patches that address security flaws.
- Strong Passwords: Implementing complex, unique passwords across devices can significantly lower the risk of unauthorized access. Using a password manager can help manage these securely.
- Network Security: Employing a robust router with WPA3 encryption and creating a separate network for smart devices can limit exposure to threats.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enabling 2FA adds an additional layer of security, requiring users to provide a second form of identification beyond just a password.
“Proactive security measures are essential in maintaining the integrity of smart home systems and protecting user data.”
User Privacy in Smart Home Systems
Ensuring user privacy is paramount in the design and implementation of smart home systems. Here are several methods to enhance privacy:
- Data Minimization: Only collect data that is necessary for the device to function, reducing the amount of personal information stored and transmitted.
- Opt-out Options: Providing users with clear options to opt out of data collection can empower them to make informed choices about their privacy.
- Transparent Policies: Companies should maintain clear, accessible privacy policies detailing how user data is collected, used, and shared.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data both in transit and at rest can protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Implications of Data Collection
The widespread use of smart home devices leads to extensive data collection, raising several implications. While this data can enhance user experience through personalization, it also poses risks related to privacy and security. Users must be aware of the following:
- Behavior Tracking: Many devices track user habits and preferences, which can be beneficial for customization but may also lead to intrusive advertising or profiling.
- Data Sharing with Third Parties: Often, data is shared with third-party companies, which can lead to privacy concerns if users are unaware of how their data is being used.
- Potential for Misuse: Collected data can be vulnerable to breaches, and if mishandled, can lead to identity theft or fraud.
- Regulatory Considerations: Increasing data protection regulations, such as GDPR, require companies to adhere to strict guidelines regarding data handling and user consent.
“Understanding the implications of data collection is vital for users to navigate the smart home landscape responsibly and securely.”
Future Trends in Smart Home Technology
The landscape of smart home technology is continually evolving, driven by advancements in innovation and changing consumer needs. As we look ahead, several trends are poised to reshape how we interact with our living spaces. This section will explore the anticipated developments in smart home design, the significant role of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and compare potential future devices to current offerings.
Predicted Developments in Smart Home Design
Emerging trends in smart home technology include increased automation, sustainability initiatives, and more user-driven customization options. Homeowners are increasingly seeking systems that not only improve comfort and convenience but also enhance energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Interactive and intuitive interfaces will become the norm, allowing users to manage multiple devices seamlessly.Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning will play a pivotal role in these transformations.
AI will facilitate predictive analytics, enabling systems to anticipate user needs based on patterns and preferences. For instance, smart thermostats may learn when a homeowner typically arrives home and adjust temperatures automatically, optimizing energy usage without sacrificing comfort.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning on Smart Homes
The integration of AI and machine learning in smart home systems will lead to significant enhancements in user experience and functionality. As these technologies evolve, smart devices will gain capabilities such as natural language processing, improving the interaction between users and their homes.One of the notable changes will be the development of more intelligent home assistants capable of understanding and executing complex commands.
These advancements will enable users to control not just individual devices but entire systems, adjusting lighting, security settings, and climate control with simple voice commands or gestures.Moreover, security improvements through AI will allow for real-time threat detection and response. Smart cameras and alarms will learn from previous incidents, adapting to new threats dynamically rather than relying solely on pre-programmed responses.
Comparison of Future Devices vs. Current Devices
The shift towards more advanced smart home technology will result in a new generation of devices that greatly outperform their predecessors. Below is a table showcasing the potential future devices compared to current versions:
| Current Device | Future Device | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Thermostat | AI-Enhanced Smart Thermostat | Predictive temperature adjustment, energy usage analytics, integration with renewable energy sources. |
| Standard Security Camera | AI-Powered Security Camera | Facial recognition, real-time threat analysis, automated alerts based on learned behavior. |
| Basic Smart Speaker | Conversational AI Hub | Contextual awareness, multi-device control, advanced voice recognition and natural language understanding. |
| Smart Light Bulb | Adaptive Smart Lighting System | Color temperature adjustment based on time of day, mood settings, energy-efficient operation based on occupancy. |
The transition towards these innovative devices underscores the potential for smarter, more efficient homes. This evolution reflects an increasing demand for technology that not only enhances comfort but also aligns with sustainable living practices, ultimately creating a more harmonious relationship between residents and their environments.
Case Studies of Successful Smart Home Implementations
The integration of smart home technology has transformed residential living, enhancing convenience, security, and energy efficiency. A few notable case studies exemplify how these technologies can be successfully implemented, significantly changing the lifestyles of homeowners.
Smart Home in Suburban Communities
One prominent example is a suburban neighborhood in California where a comprehensive smart home system was deployed in multiple homes. This system included smart thermostats, security cameras, and automated lighting. Homeowners reported a remarkable shift in their daily routines, where energy consumption was optimized, reducing bills by approximately 30%. The key components of this implementation included:
- Smart Thermostats: Homeowners could control heating and cooling remotely, adapting settings according to their schedules.
- Automated Security Systems: Enhanced security features like motion detection and remote monitoring increased homeowners’ peace of mind.
- Smart Lighting: Automated lighting systems allowed for energy savings and improved ambiance through customizable settings.
A significant lesson learned from this case was the importance of user-friendly interfaces. Homeowners expressed that the ease of controlling devices through a single app was crucial for adoption, reinforcing the need for seamless integration in future designs.
Urban Apartment Complex with Integrated Smart Systems
Another successful implementation was in an urban apartment complex in New York City, where smart technology was integrated into the design of new units. This complex featured smart locks, intelligent energy meters, and in-home voice assistants. Residents experienced enhanced connectivity and a sense of community through shared smart amenities.Key impacts included:
- Smart Locks: Residents enjoyed the convenience of keyless entry and the ability to grant temporary access to guests.
- Intelligent Energy Meters: Real-time energy usage data allowed tenants to monitor their consumption and adjust habits accordingly.
- Voice Assistants: Integration with home automation simplified daily tasks, leading to increased satisfaction among residents.
This case taught developers the value of community-oriented smart systems. Implementing features that encourage interaction among residents can enhance the overall living experience and promote a stronger community bond.
Retrofitting Existing Homes with Smart Technology
A third case study focused on retrofitting existing homes in an older neighborhood in Texas. Homeowners opted to upgrade their traditional homes with smart devices like smart thermostats, leak detectors, and energy-efficient appliances. This initiative not only boosted the homes’ market values but also improved the overall comfort of living.The benefits observed included:
- Leak Detectors: Early detection of plumbing issues helped homeowners avoid costly repairs and water damage.
- Energy-Efficient Appliances: Replacing old appliances with smart models led to significant energy savings and cost reductions.
- Smart Thermostats: Homeowners could manage heating and cooling effectively, resulting in improved comfort levels.
The lessons from this retrofitting project highlight the necessity of educating homeowners about available technologies. Providing information on use and benefits can enhance user experience and foster greater acceptance of smart home technologies.
User Feedback and Iterative Design in Smart Homes
Source: techterms.com
User feedback plays a crucial role in the design and development of smart home technologies. As these devices become increasingly integrated into daily life, understanding user experiences, preferences, and pain points becomes essential. Effective feedback collection allows designers to create more intuitive and user-friendly products that cater to the needs of their users.Iterative design is an approach that emphasizes continuous improvement based on user feedback.
This process not only enhances user satisfaction but also bolsters device functionality, ensuring that smart home devices evolve in alignment with user expectations. By incorporating feedback at various stages of the design process, developers can identify and rectify issues early, leading to a more refined final product.
Methods for Collecting User Feedback on Smart Home Technologies
Gathering user feedback is vital for refining smart home devices. There are various methodologies that can be employed to effectively collect this feedback:
- User Surveys: Simple questionnaires can be distributed to users post-installation to gauge their satisfaction and gather insights on their experience.
- Focus Groups: Bringing together a small group of users allows for in-depth discussions about specific features and overall usability.
- Usability Testing: Observing users interact with the technology in real-time can unveil usability issues that might not surface in surveys.
- Feedback Apps: Dedicated applications or platforms where users can report issues and suggest improvements directly related to their experience.
- Online Reviews: Analyzing reviews on retail platforms can provide valuable insight into common user challenges and praises.
- Customer Support Interactions: Monitoring inquiries and complaints can help identify recurring problems that need attention.
Iterative design enhances user satisfaction by incorporating feedback into each development cycle. Devices are not only tested for performance but are also adjusted based on real-world usage. Such practices encourage a culture of continuous improvement, where user preferences shape the evolution of smart technologies. As a result, devices become more intuitive and effective, ultimately leading to higher user engagement and loyalty.
Outcome Summary
In summary, the exploration of Smart home technology design reveals a dynamic landscape where innovation meets user-centered design. As we look to the future, embracing advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning will continue to enhance our smart living experiences. By focusing on integration, security, and user feedback, we can ensure that our homes evolve into truly intelligent spaces that cater to our every need.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is smart home technology?
Smart home technology refers to devices and systems that connect to the internet, allowing homeowners to control and monitor their home environment remotely.
How do smart home devices communicate with each other?
Smart home devices typically communicate via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or Zigbee, using standard protocols that allow for seamless integration.
Are smart homes safe from cyber threats?
While smart homes can be vulnerable to cyber threats, implementing strong security measures such as updated software, secure passwords, and proper network configurations can mitigate risks.
Can I control smart home devices with my smartphone?
Yes, most smart home devices come with mobile applications that allow users to control features and settings directly from their smartphones.
What are the benefits of having a smart home?
The benefits of a smart home include increased convenience, enhanced security, energy efficiency, and the ability to manage devices remotely, leading to a more comfortable living environment.








